Introduction
First of all, I would like to thank all the readers who have read and voted for my articles. In the Beginner's Guide series, I have written some articles on state management. Probably this is my last article on state management.
This article will give you a very good understanding of session. In this article, I have covered the basics of session, different ways of storing session objects, session behavior in web farm scenarios, session on Load Balancer, etc. I have also explained details of session behavior in a live production environment. Hope you will enjoy this article and provide your valuable suggestions and feedback.
What is Session?
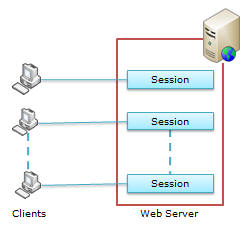
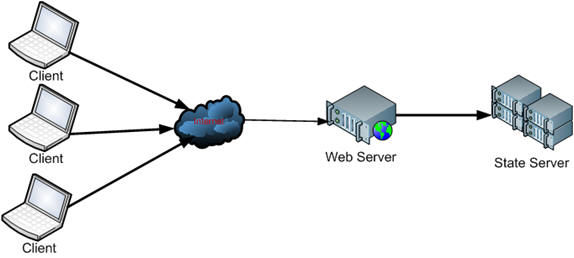
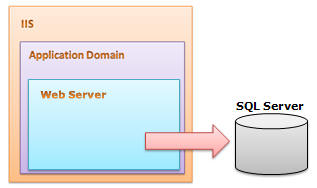
Web is stateless, which means a new instance of a web page class is re-created each time the page is posted to the server. As we all know, HTTP is a stateless protocol, it can't hold client information on a page. If the user inserts some information and move to the next page, that data will be lost and the user would not be able to retrieve that information. What do we need here? We need to store information. Session provides a facility to store information on server memory. It can support any type of object to store along with our own custom objects. For every client, session data is stored separately, which means session data is stored on a per client basis. Have a look at the following diagram:
Fig: For every client, session data is stored separately
State management using session is one of the best ASP.NET features, because it is secure, transparent from users, and we can store any kind of object in it. Along with these advantages, some times session can cause performance issues in high traffic sites because it is stored in server memory and clients read data from the server. Now let's have a look at the advantages and disadvantages of using session in our web applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of Session?
Following are the basic advantages and disadvantages of using session. I have describe in details with each type of session at later point of time.
Advantages:
- It helps maintain user state and data all over the application.
- It is easy to implement and we can store any kind of object.
- Stores client data separately.
- Session is secure and transparent from the user.
Disadvantages:
- Performance overhead in case of large volumes of data/user, because session data is stored in server memory.
- Overhead involved in serializing and de-serializing session data, because in the case of
StateServer and SQLServer session modes, we need to serialize the objects before storing them.
Besides these, there are many advantages and disadvantages of session that are based on the session type. I have discussed all of them in the respective sections below.
Storing and retrieving values from Session
Storing and retrieving values in session are quite similar to that in ViewState. We can interact with session state with the System.Web.SessionState.HttpSessionState class, because this provides the built-in session object in ASP.NET pages.
The following code is used for storing a value to session:
Hide Copy Code
Session["UserName"] = txtUser.Text;
Now, let's see how we can retrieve values from session:
Hide Copy Code
if (Session["UserName"] != null)
{
lblWelcome.Text = "Welcome : " + Session["UserName"];
}
else
{
}
We can also store other objects in session. The following example shows how to store a DataSet in session.
Hide Copy Code
Session["DataSet"] = _objDataSet;
The following code shows how we to retrieve that DataSet from session:
Hide Copy Code
if (Session["DataSet"] != null)
{
DataSet _MyDs = (DataSet)Session["DataSet"];
}
else
{
}
References:
Session ID
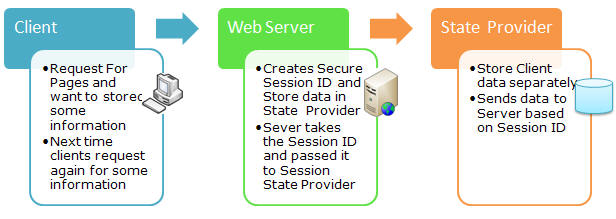
ASP.NET uses an 120 bit identifier to track each session. This is secure enough and can't be reverse engineered. When a client communicates with a server, only the session ID is transmitted between them. When the client requests for data, ASP.NET looks for the session ID and retrieves the corresponding data. This is done in the following steps:
- Client hits the web site and information is stored in the session.
- Server creates a unique session ID for that client and stores it in the Session State Provider.
- The client requests for some information with the unique session ID from the server.
- Server looks in the Session Providers and retrieves the serialized data from the state server and type casts the object.
Take a look at the the pictorial flow:
Fig: Communication of client, web server, and State Provider
References:
Session Mode and State Provider
In ASP.NET, there are the following session modes available:
- InProc
- StateServer
- SQLServer
- Custom
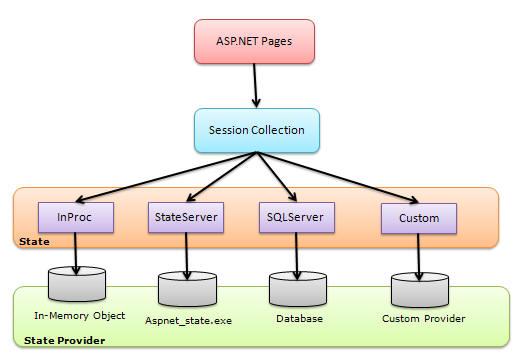
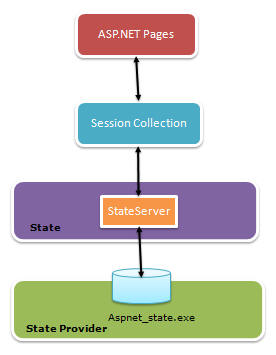
For every session state, there is a Session Provider. The following diagram will show you how they are related:
Fig: Session state architecture
We can choose the session state provider based on which session state we are selecting. When ASP.NET requests for information based on the session ID, the session state and its corresponding provider are responsible for sending the proper information. The following table shows the session mode along with the provider name:
| Session State Mode | State Provider |
| InProc | In-memory object |
| StateServer | Aspnet_state.exe |
| SQLServer | Database |
| Custom | Custom provider |
Apart from that, there is another mode Off. If we select this option, the session will be disabled for the application. But our objective is to use session, so we will look into the above four session state modes.
Session States
Session state essentially means all the settings that you have made for your web application for maintaining the session. Session State itself is a big thing. It says all about your session configuration, either in the web.config or from the code-behind. In the web.config, <SessionState> elements are used for setting the configuration of the session. Some of them are Mode, Timeout, StateConnectionString, CustomProvider, etc. I have discussed about each and every section of the connection string. Before I discuss Session Mode, take a brief overview of session events.
Session Event
There are two types of session events available in ASP.NET:
Session_StartSession_End
You can handle both these events in the global.asax file of your web application. When a new session initiates, the session_start event is raised, and the Session_End event raised when a session is abandoned or expires.
Hide Copy Code
void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
References:
Session Mode
I have already discussed about session modes in ASP.NET. Following are the different types of session modes available in ASP.NET:
OffInProcStateServerSQLServerCustom
If we set session Mode="off" in web.config, session will be disabled in the application. For this, we need to configure web.config the following way:
InProc Session Mode
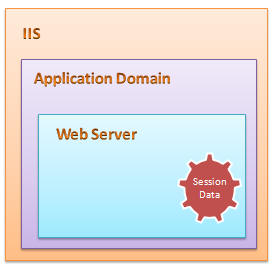
This is the default session mode in ASP.NET. Its stores session information in the current Application Domain. This is the best session mode for web application performance. But the main disadvantage is that, it will lose data if we restart the server. There are some more advantages and disadvantages of the InProc session mode. I will come to those points later on.
Overview of InProc session mode
As I have already discussed, in InProc mode, session data will be stored on the current application domain. So it is easily and quickly available.
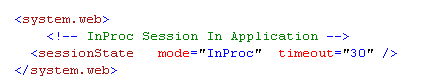
InProc session mode stores its session data in a memory object on the application domain. This is handled by a worker process in the application pool. So if we restart the server, we will lose the session data. If the client request for data, the state provider read the data from an in-memory object and returns it to the client. In web.config, we have to mention the session mode and also set the timeout.
The above session timeout setting keeps the session alive for 30 minute. This is configurable from the code-behind too.
Hide Copy Code
Session.TimeOut=30;
There are two types of session events available in ASP.NET: Session_Start() and Session_End and this is the only mode that supports the Session_End() event. This event is called after the session timeout period is over. The general flow for the InProc session state is like this:
When the Session_End() is called depends on the session timeout. This is a very fast mechanism because no serialization occurs for storing and retrieving data, and data stays inside the same application domain.
When should we use the InProc session mode?
InProc is the default session mode. It can be very helpful for a small web site and where the number of users is very less. We should avoid InProc in a Web Garden scenario (I will come to this topic later on).
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- It store session data in a memory object of the current application domain. So accessing data is very fast and data is easily available.
- There is not requirement of serialization to store data in InProc session mode.
- Implementation is very easy, similar to using the ViewState.
Disadvantages:
Although InProc session is the fastest, common, and default mechanism, it has a lot of limitations:
- If the worker process or application domain is recycled, all session data will be lost.
- Though it is the fastest, more session data and more users can affect performance, because of memory usage.
- We can't use it in web garden scenarios.
- This session mode is not suitable for web farm scenarios.
As per the above discussion, we can conclude that InProc is a very fast session storing mechanism but suitable only for small web applications. InProc session data will get lost if we restart the server, or if the application domain is recycled. It is also not suitable for Web Farm and Web Garden scenarios.
Now we will have a look the other options available to overcome these problems. First comes the StateServer mode.
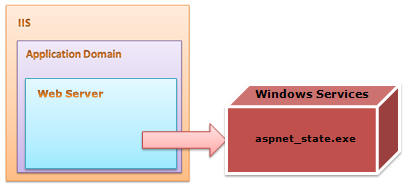
StateServer Session Mode
Overview of StateServer session mode
This is also called Out-Proc session mode. StateServer uses a stand-alone Windows Service which is independent of IIS and can also be run on a separate server. This session state is totally managed by aspnet_state.exe. This server may run on the same system, but it's outside of the main application domain where your web application is running. This means if you restart your ASP.NET process, your session data will still be alive. This approaches has several disadvantages due to the overhead of the serialization and de-serialization involved, it also increases the cost of data access because every time the user retrieves session data, our application hits a different process.
Configuration for StateServer session mode
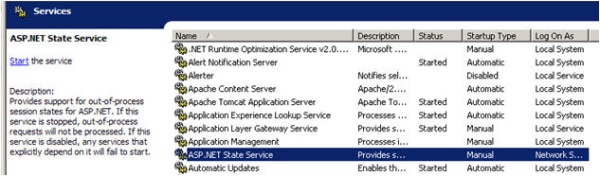
In StateServer mode, session data is stored in a separate server which is independent of IIS and it is handled by aspnet_state.exe. This process is run as a Windows Service. You can start this service from the Windows MMC or from the command prompt.
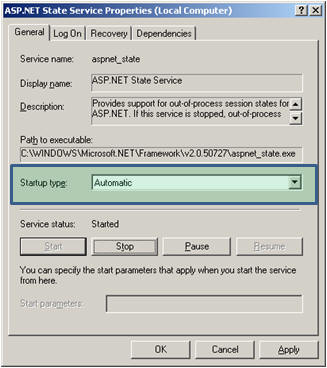
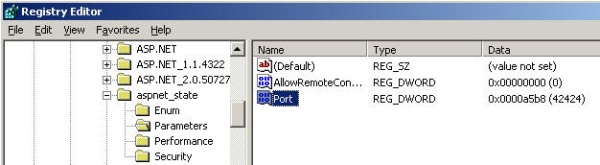
By default, the "Startup Type" of the ASP.NET state service is set to Manual; we have to set it to Automatic.
From the command prompt, just type "net start aspnet_state". By default, this service listens to TCP port 42424, but we can change the port from the Registry editor as show in the picture below:
Now have a look at the web.config configuration for the StateServer setting. For the StateServer setting, we need to specify the stateConnectionString. This will identify the system that is running the state server. By default, stateConnectionString used the IP 127.0.0.1 (localhost) and port 42424.
When we are using StateServer, we can configure the stateNetworkTimeOut attribute to specify the maximum number of seconds to wait for the service to respond before canceling the request. The default timeout value is 10 seconds.
For using StateServer, the object which we are going to store should be serialized, and at the time of retrieving, we need to de-serialize it back. I have described this below with an example.
How the StateServer Session Mode works
We use the StateServer session mode to avoid unnecessary session data loss when restarting our web server. StateServer is maintained by the aspnet_state.exe process as a Windows service. This process maintains all the session data. But we need to serialize the data before storing it in StateServer session mode.
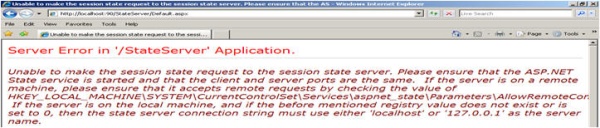
As shown in the above figure, when the client sends a request to the web server, the web server stores the session data on the state server. The StateServer may be the current system or a different system. But it will be totally independent of IIS. The destination of the StateServer will depend on the web.configstateConnectionString setting. If we set it to 127.0.0.1:42424, it will store data in the local system itself. For changing the StateServer destination, we need to change the IP, and make sure aspnet_state.exe is up and running on that system. Otherwise you will get the following exception while trying to store data on session.
When we are storing an object on session, it should be serialized. That data will be stored in the StateServer system using the State Provider. And at the time of retrieving the data, the State Provider will return the data. The complete flow is given in the picture below:
Example of StateServer Session Mode
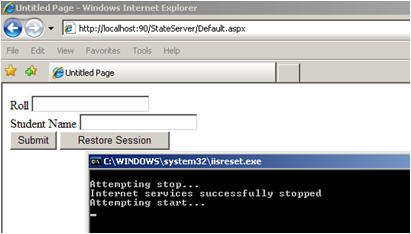
Here is a simple example of using the StateServer session mode. I have created this sample web application directly on IIS so that we can easily understand its usage.
Step 1: Open Visual Studio > File > New > Web Sites. Choose Location as HTTP and create the web application.
Now if you open IIS, you will see a virtual directory created with the name of your web application, in my case it is StateServer.
Step 2: Create s simple UI that will take the roll number and the name of a student. We will store the name and roll number in a state server session. I have also created a class StudentInfo. This class is listed below:
Hide Shrink  Copy Code
Copy Code
[Serializable]
public class StudentInfo
{
public StudentInfo()
{
}
public StudentInfo(int intRoll, string strName)
{
this.Roll = intRoll;
this.Name = strName;
}
private int intRoll;
private string strName;
public int Roll
{
get
{
return intRoll;
}
set
{
intRoll = value;
}
}
public string Name
{
get
{
return strName;
}
set
{
strName = value;
}
}
}
Now have a look at the code-behind. I have added two buttons: one for storing session and another for retrieving session.
Hide Copy Code
protected void btnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StudentInfo _objStudentInfo =
new StudentInfo(Int32.Parse( txtRoll.Text) ,txtUserName.Text);
Session["objStudentInfo"] = _objStudentInfo;
ResetField();
}
protected void btnRestore_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StudentInfo _objStudentInfo = (StudentInfo) Session["objStudentInfo"];
txtRoll.Text = _objStudentInfo.Roll.ToString();
txtUserName.Text = _objStudentInfo.Name;
}
Step 3: Configure your web.config for state server as I have already explained. And please make sure aspnet_state.exe is up and running on the configured server.
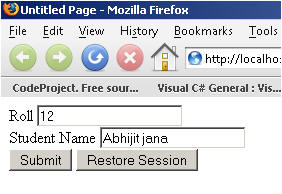
Step 4: Run the application.
Enter the data, click on Submit.
There are the following tests that I have made which will totally explain how exactly StateServer is useful.
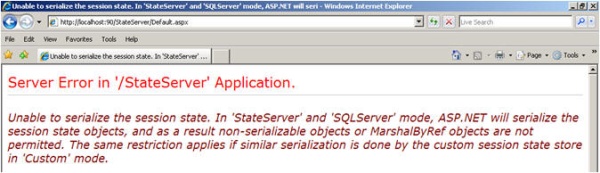
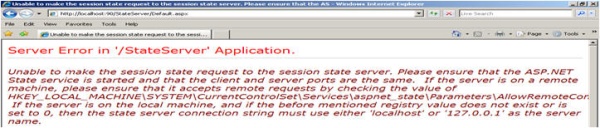
First: Remove the [Serializable ] keyword from the StudentInfo class and try to run the application. When you click on the Submit button, you will get the following error:
Which clearly says that you have to serialize the object before storing it.
Second: Run the application, store data by clicking on the Submit button. Restart IIS.
In the case of InProc, you will have already lost your session data, but with StateServer, click on Restore Session and you will get your original data, because StateServer data does not depend on IIS. It keeps it separately.
Third: Stop aspnet_state.exe from the Windows Services MMC and submit the data. You will get the following error:
because your State Server process is not running. So please keep in mind these three points when using StateServer mode.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Based on the above discussion:
Advantages:
- It keeps data separate from IIS so any issues with IIS will not hamper session data.
- It is useful in web farm and web garden scenarios.
Disadvantages:
- Process is slow due to serialization and de-serialization.
- State Server always needs to be up and running.
I am stopping here on StateServer, you will find some more interesting points on it in the Load Balancer, Web Farm, and Web Garden section.
References:
SQLServer Session Mode
Overview of SQL Server Session Mode
This session mode provide us more secure and reliable session management in ASP.NET. In this session mode, session data is serialized and stored in A SQL Server database. The main disadvantage of this session storage method is the overhead related with data serialization and de-serialization. It is the best option for using in web farms though.
To setup SQL Server, we need these SQL scripts:
- For installing: InstallSqlState.sql
- For uninstalling: UninstallSQLState.sql
The easiest way to configure SQL Server is using the aspnet_regsql command.
I have explained in detail the use of these files in the configuration section. This is the most useful state management in web farm scenarios.
When should we use SQLServer Session Mode?
- SQL Server session mode is a more reliable and secure session state management.
- It keeps data in a centralized location (database).
- We should use the SQLServer session mode when we need to implement session with more security.
- If there happens to be frequent server restarts, this is an ideal choice.
- This is the perfect mode for web farm and web garden scenarios (I have explained this in detail later).
- We can use SQLServer session mode when we need to share session between two different applications.
Configuration for SQLServer Session Mode
In SQLServer session mode, we store session data in SQL Server, so we need to first provide the database connection string in web.config. The sqlConnectionString attribute is used for this.
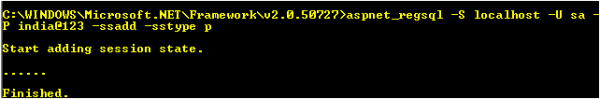
After we setup the connection string, we need to configure the SQL Server. I will now explain how to configure your your SQL Server using the aspnet_regsql command.
Step 1: From command prompt, go to your Framework version directory. E.g.: c:\windows\microsoft.net\framework\<version>.
Step 2: Run the aspnet_regsql command with the following parameters:
Have a look at the parameters and their uses:
| Parameters | Description |
| -ssadd | Add support for SQLServer mode session state. |
| -sstype p | P stands for Persisted. It persists the session data on the server. |
| -S | Server name. |
| -U | User name. |
| -P | Password. |
After you run the command, you will get the following message:
That's all.
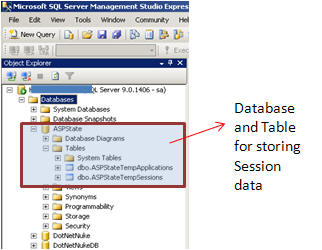
Step 3: Open SQL Server Management Studio, check if a new database ASPState has been created, and there should be two tables:
- ASPStateTempApplications
- ASPStateTempSessions
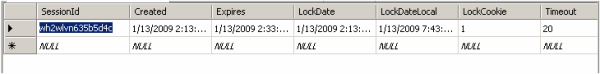
Change the configuration string of the StateServer example and run the same sample application.
Just store the roll number and user name and click on the Submit button. Open the ASPStateTempSessions table from SQL Server Management Studio.. here is your session data:
Now do the following test that I have already explained in the StateServer mode section:
- Remove the
Serialize keyword from the StydentInfo class
- Reset IIS and click on Restore Session
- Stop SQL Server Services
I think I have explained the SQLServer session mode well.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Session data not affected if we restart IIS.
- The most reliable and secure session management.
- It keeps data located centrally, is easily accessible from other applications.
- Very useful in web farms and web garden scenarios.
Disadvantages:
- Processing is very slow in nature.
- Object serialization and de-serialization creates overhead for the application.
- As the session data is handled in a different server, we have to take care of SQL Server. It should be always up and running.
References:
Custom Session Mode
Overview of Custom Session Mode
Commonly we use the InProc, StateServer, or SQLServer session modes for our application, but we also need to know the fundamentals of the Custom session mode. This session mode is quite interesting, because Custom session gives full control to us to create everything, even the session ID. You can write your own algorithm to generate session IDs.
You can implement custom providers that store session data in other storage mechanisms simply by deriving from the SessionStateStoreProviderBase class. You can also generate a new session ID by implementing ISessionIDManager.
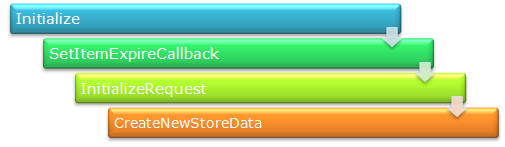
These are the methods called during the implementation of Custom session:
In the Initialize method, we can set a custom provider. This will initialize the connection with that provider. SetItemExpireCallback is used to set SessionTimeOut. We can register a method that will be called at the time of session expiration. InitializeRequest is called on every request and CreateNewStoreData is used to create a new instance of SessionStateStoreData.
When should we use Custom Session Mode?
We can use Custom session mode in the following cases:
- We want to store session data in a place other than SQL Server.
- When we have to use an existing table to store session data.
- When we need to create our own session ID.
What configuration do we need for it?
We need to configure our web.config like this:
If you want to explore this more, please check the References section.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- We can use an existing table for storing session data. This is useful when we have to use an existing database.
- It's not dependent on IIS, so restarting the web server does not have any effect on session data.
- We can crate our own algorithm for generating session ID.
Disadvantages:
- Processing of data is very slow.
- Creating a custom state provider is a low-level task that needs to be handled carefully to ensure security.
It is always recommended to use a third party provider rather than create your own.
References:
Overview of production deployment
Production environments are where we deploy our applications on a live production server. It is a major and big challenge for web developers to deploy their applications on a live server, because in a big production environment, there are a large number of users and it is hard to handle the load for so many users with a single server. Here comes in the concepts of Web Farm, Load Balancer, Web Garden, etc.
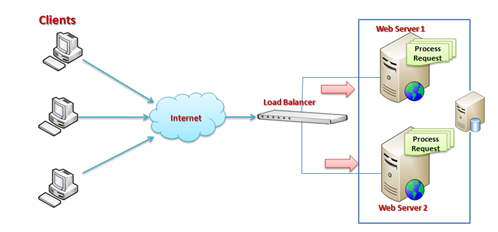
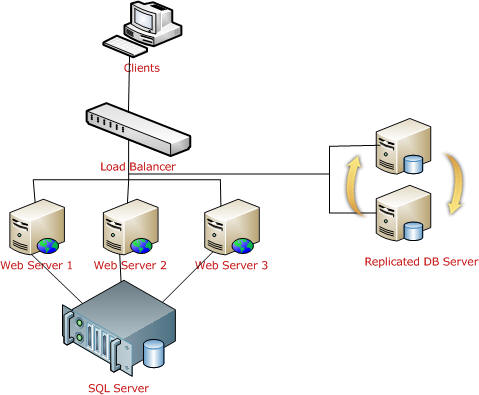
Just a few months back, I deployed a web application in a live production environment which is accessed by millions of user and there were more than 10 Active Directory instances, more than 10 web servers over a Load Balancer, and several database server, Exchange Server, LCS Server, etc. The major risk involved in multiple servers is session management. The following picture shows a general diagram of production environments:
I will try to explain the different scenarios that you need to keep in mind while deploying your application.
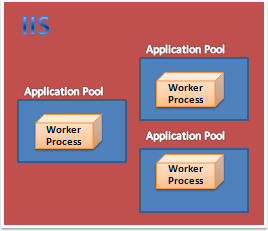
Application Pool
This is one of the most important things you should create for your applications in a production environment. Application pools are used to separate sets of IIS worker processes that share the same configuration. Application pools enable us to isolate our web application for better security, reliability, and availability. The worker process serves as the process boundary that separates each application pool so that when one worker process or application has an issue or is recycled, other applications or worker processes are not affected.
Identity of Application Pool
Application pool identity configuration is an important aspect of security in IIS 6.0 and IIS 7.0, because it determines the identity of the worker process when the process is accessing a resource. In IIS 7.0, there are three predefined identities that are the same as in IIS 6.0.
| Application Pool Identity | Description |
LocalSystem |
Built-in account that has administrative privileges on the server. It can access both local and remote resources. For any kind accessing of server files or resources, we have to set the identity of the application pool to LocalSystem.
|
LocalServices | Built-in account has privileges of an authenticated local user account. It does not have any network access permission. |
NetworkServices | This is the default identity of Application Pool. NetworkServices has the privileges of an authenticated local user account. |
Creating and assigning Application Pool
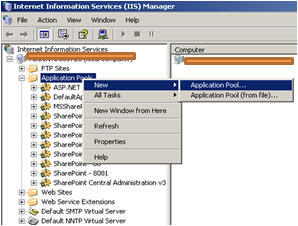
Open IIS Console, right click on Application Pool Folder > Create New.
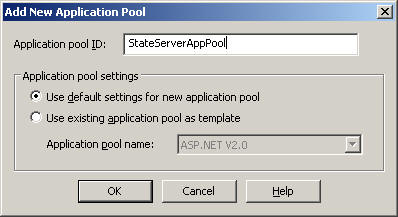
Give the Application Pool ID and click OK.
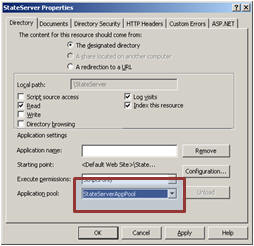
Now, right click on the Virtual Directory (I am using StateServer web sites) and assign StateServerAppPool to the StateServer Virtual Directory.
So this StateServer web site will run independently with StateServerAppPool. Any problem related with other applications will not affect this application. This is the main advantage of creating application pools separately.
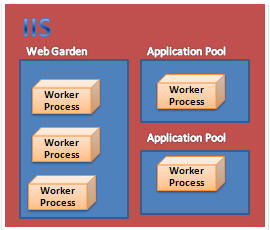
Web Garden
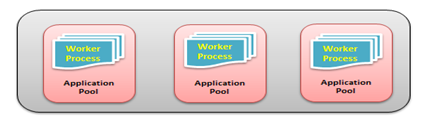
By default, each application pool runs with a single worker process (W3Wp.exe). We can assign multiple worker processes with a single application pool. An application pool with multiple worker processes is called a Web Garden. Many worker processes with the same Application Pool can sometimes provide better throughput performance and application response time. And each worker process should have its own Thread and memory space.
As shown in the picture, in IIS, there may be multiple application pools and each application pool will have at least one worker process. A Web Garden should contain multiple worker processes.
There are certain restrictions in using a Web Garden with your web application. If we use the InProc session mode, our application will not work correctly because the session will be handled by a different worker process. To avoid this problem, we should use the OutProc session mode and we can use a session state server or SQL-Server session state.
Main advantage: The worker processes in a Web Garden share the requests that arrive for that particular application pool. If a worker process fails, another worker process can continue processing the requests.
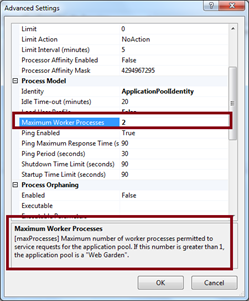
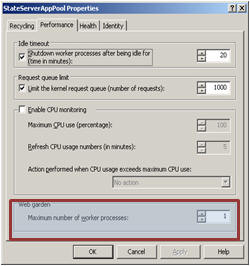
How to Create a Web Garden?
Right click on Application Pool > Go to Performance tab > Check Web Garden section (highlighted in picture):
By default, it would be 1. Just change it to more than one.
How Session depends on Web Garden?
I have already explained that InProc is handled by a worker process. It keeps data inside its memory object. Now if we have multiple worker processes, then it would be very difficult to handle the session because each and every worker process has its own memory, so if my first request goes to WP1 and it keeps my session data and the second request goes to WP2, I am trying to retrieve session data and it will not be available, which will throw an error. So please avoid Web Gardens in InProc session mode.
We can use StateServer or SQLServer session modes in Web Gardens because as I have already explained, these two session modes do not depend on worker processes. In my example, I have also explained that if you restart IIS, you are still able to access your session data.
In short:
| Session Mode | Recommended |
| InProc | No |
| StateServer | Yes |
| SQLServer | Yes |
Web Farm and Load Balancer
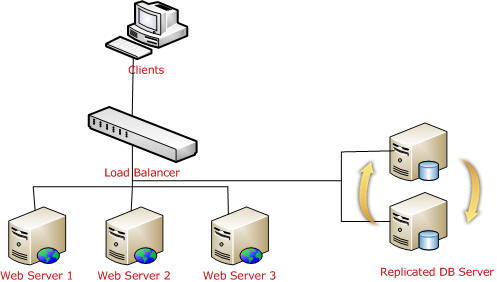
This is the most common terms that are used in production deployments. These terms come in when we are using multiple web servers for deploying our applications. The main reason for using these is we have to distribute the load over multiple servers. A Load Balancer is used to distribute the load on multiple servers.
If we take a look at the above diagram, the client request the URL and it will hit a Load Balancer, which decides which server to access. The load balancer will distribute the traffic over all the different web servers.
Now how does this affect Session?
Handling Session in web farm and load balancer scenarios
Handling session is one of the most challenging jobs in a web farm.
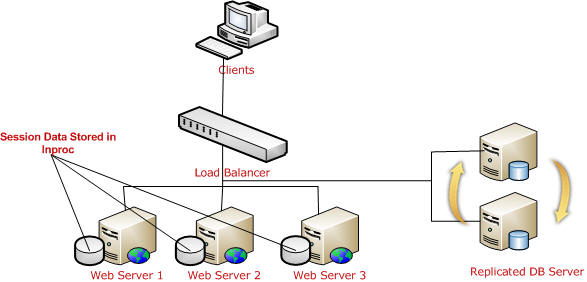
InProc: In InProc session mode, session data is stored in an in-memory object of the worker process. Each server will have its own worker process and will keep session data inside its memory.
If one server is down, and if the request goes to a different server, the user is not able to get session data. So it is not recommended to use InProc in Web Farms.
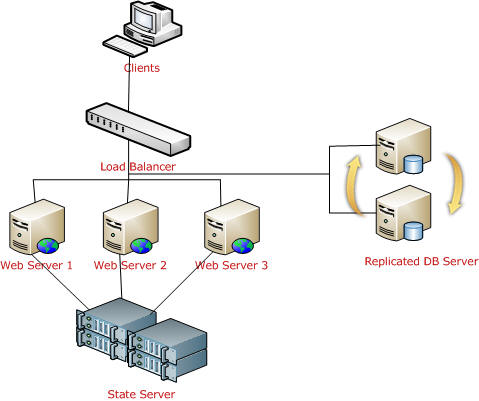
StateServer: I have already explained what a state server is and how to configure a state server, etc. For web farm scenarios, you can easily understand how much this is important because all session data will be stored in a single location.
Remember, in a web farm, you have to make sure you have the same <machinekey> in all your web servers. Other things are the same as I have describe earlier. All web.config files will have the same configuration (stateConnectionString) for session state.
SQL Server: This is another approach, the best that we can use in a web farm. We need to configure the database first. The required steps have been explained covered.
As shown in the above picture, all web server session data will be stored in a single SQL Server database. And it is easily accessible. Keep one thing in mind, you should serialize objects in both StateServer and SQLServer modes. If one of the web servers go down, the load balancer will distribute the load to other servers and the user will still be able to read session data from the server, because data is stored in a centralized database server.
In summary, we can use either StateServer or SQLServer session mode in a web farm. We should avoid InProc.
Session and Cookies
Clients use cookies to work with session. Because clients need to present the appropriate session ID with each request. We can do this in the following ways:
Using cookies
ASP.NET creates a special cookie named ASP.NET_SessionId automatically when a session collection is used. This is the default. Session ID is transmitted through that cookie.
Cookie munging
Some older browsers do not support cookies or the user may disable cookies in the browser, in that case, ASP.NET transmits session ID in a specially modified (or “munged”) URL.
How Cookie Munging works?
When the user requests for a page on a server, the server encoded the session ID and adds it with every HREF link in the page. When the user clicks on a link, ASP.NET decodes that session ID and passes it to the page that the user is requesting. Now the requesting page can retrieve session variables. This all happens automatically if ASP.NET detects that the user's browser does not support cookies.
How to implement Cookie Munging?
For this, we have to make our session state cookie-less.
Removing Session
Following are the list of methods that are used to remove Session:
| Method | Description |
Session.Remove(strSessionName); | Removes an item from the session state collection. |
Session.RemoveAll() | Removes all items from the session collection. |
Session.Clear() | Remove all items from session collection. Note: There is no difference between Clear and RemoveAll. RemoveAll() calls Clear() internally. |
Session.Abandon() | Cancels the current session. |
Enabling and disabling Session
For performance optimization, we can enable or disable session because each and every page read and write access of the page involves some performance overhead. So it is always better to enable and disable session based on requirements rather than enable it always. We can enable and disable session state in two ways:
- Page level
- Application level
Page level
We can disable session state in page level using the EnableSessionState attribute in the Page directive.
This will disable the session activities for that particular page.
The same way, we can make it read-only also. This will permit to access session data but will not allow writing data on session.
Application level
Session state can be disabled for the entire web application using the EnableSessionState property in Web.Config.
Generally we use page level because some pages may not require any session data or may only read session data.
References:
Summary
Hope you are now really familiar with Session, its use, how to apply it in web farms, etc. To summarise:
- The in-process (InProc) session provider is the fastest because of everything being stored inside memory. Session data will be lost if we restart the web server or if the worker process is recycled. You can use this in small web applications where the number of users is less. Do not use InProc in web farms.
- In StateServer session mode, session data is maintained by aspnet_state.exe. It keeps session data out of the web server. So any issues with the web server does not affect session data. You need to serialized an object before storing data in StateServer session. We can use this safely in web farms.
- SQLServer session modes store data in SQL Server. We need to provide the connection string. Here we also need to serialize the data before storing it to session. This is very useful in production environments with web farms.
- We can use a Custom provider for custom data sources or when we need to use an existing table to store session data. We can also create custom session IDs in Custom mode. But it is not recommended to create your own custom provider. It is recommended to use a third party provider.
Hope you have enjoyed the article. Please give your suggestions and feedback for further improvements. Again thanks for reading.